9.3 Earth’s Field Physical Geology

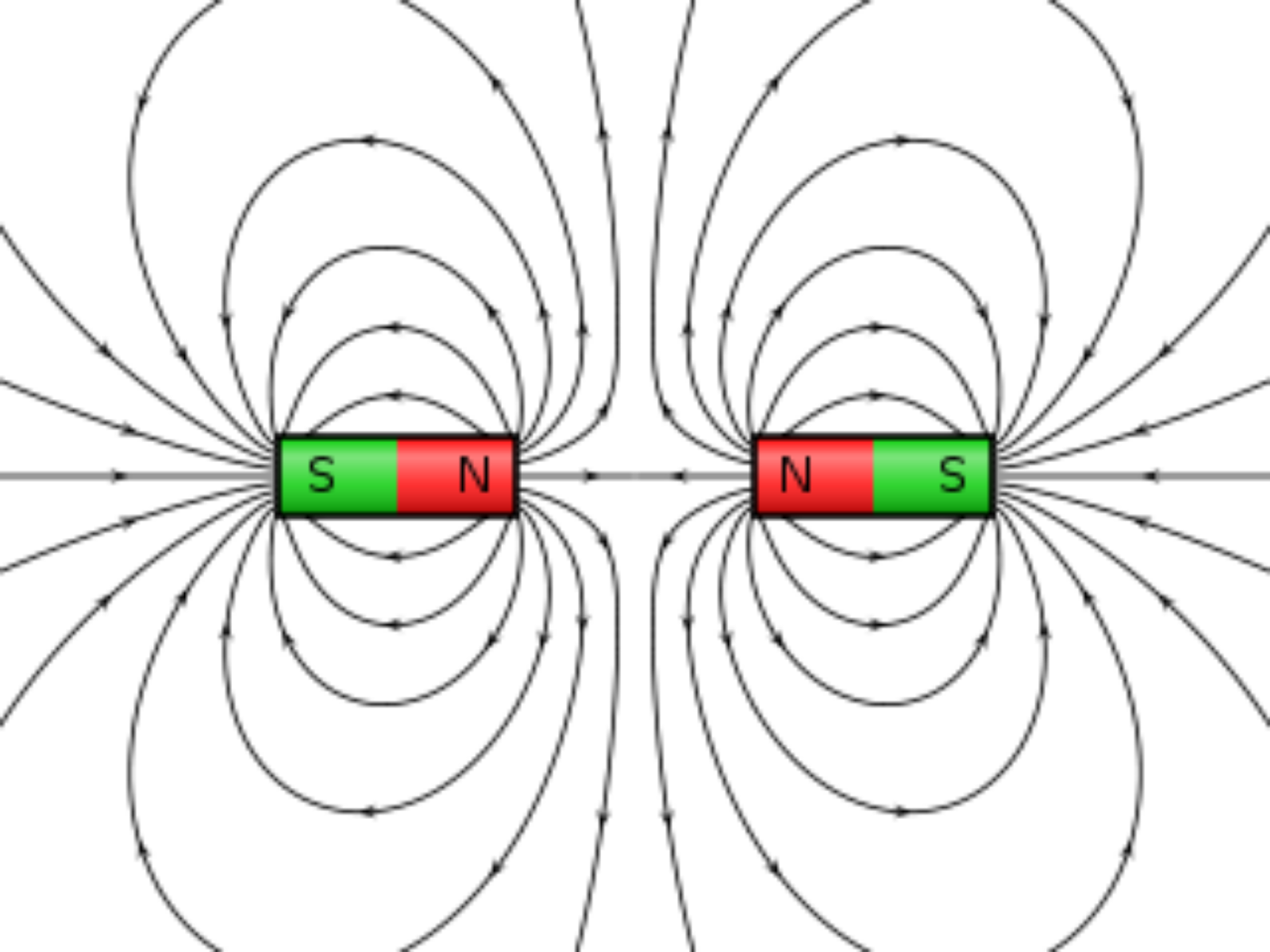
Diagram of field lines. Opposite poles attract, and like poles repel Stock Photo Alamy
F = qvBsinθ F = q v B sin θ. 11.2. where θ is the angle between the velocity and the magnetic field. The SI unit for magnetic field strength B is called the tesla (T) after the eccentric but brilliant inventor Nikola Tesla (1856-1943), where. 1T = 1N A ⋅ m. 1 T = 1 N A · m.
How does a work?
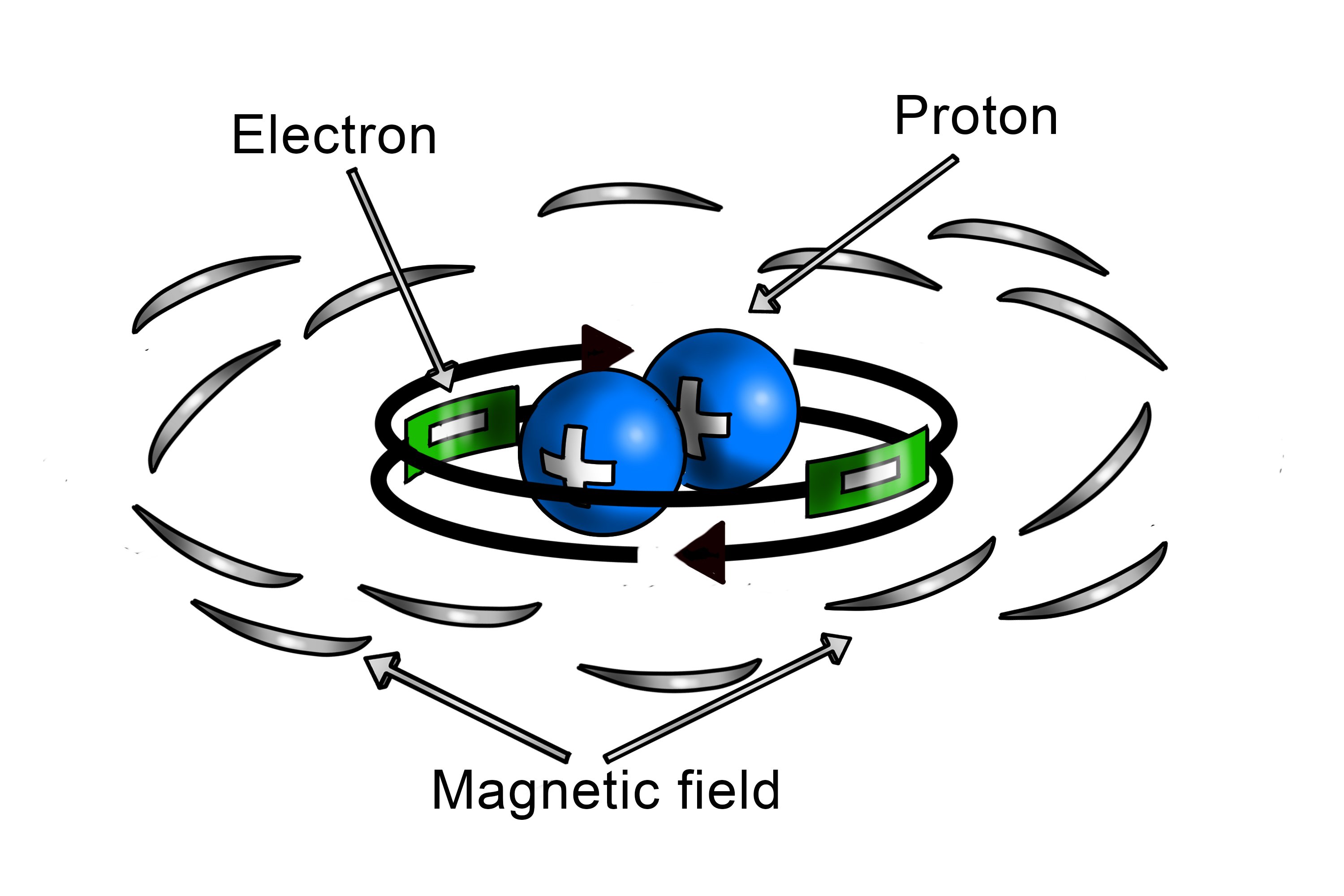
Magnetic fields Magnetic fields arise from permanent magnets and electric charges in motion. Magnets can occur naturally (such as the Earth's magnetic field), or they can be made by magnetizing ferromagnetic materials. Magnetic fields ultimately are the result of the motion of charges.
Introduction to (Revision) SPM Physics Form 4/Form 5 Revision Notes
A magnetic field is a picture that we use as a tool to describe how the magnetic force is distributed in the space around and within something magnetic. [Explain] Most of us have some familiarity with everyday magnetic objects and recognize that there can be forces between them.
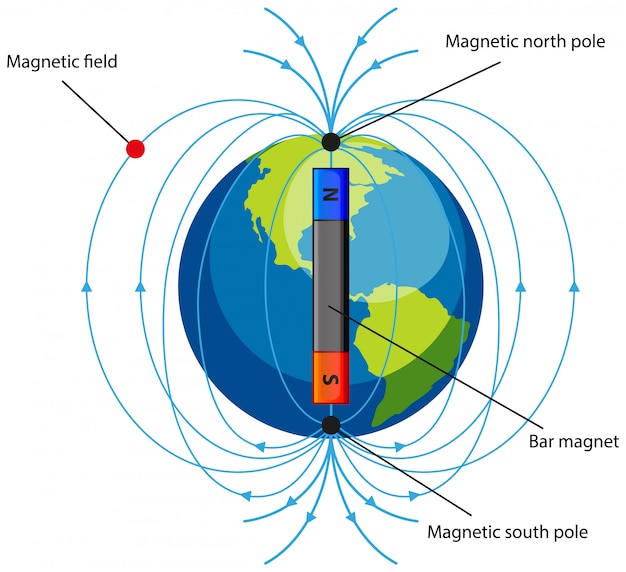
Diagram showing field on white Vector Free Download
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, [1] : ch1 [2] and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field.
Field Lines Definition, Properties, How to Draw Teachoo
A magnetic field is a vector field in the neighbourhood of a magnet, electric current, or changing electric field in which magnetic forces are observable. A magnetic field is produced by moving electric charges and intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property known as spin.

Diagram showing earth field Royalty Free Vector
The equation that gives the force on a charge moving at a velocity v in a magnetic field B is: This is a vector equation : F is a vector, v is a vector, and B is a vector. The only thing that is not a vector is q. Note that when v and B are parallel (or at 180°) to each other, the force is zero. The maximum force, F = qvB, occurs when v and B.

Electrical Academia
Lesson 1: Magnetism of magnets and wires Intro to magnetic fields (Why fields?) Magnetic field lines: direction Magnetic field lines: special properties Magnetic field lines: field strength Science > Electromagnetism (Essentials) - Class 12th > Why are magnets magnetic? And why are other things not? > Magnetism of magnets and wires
Physics science about the movement of fields Positive and negative. 593998 Vector Art
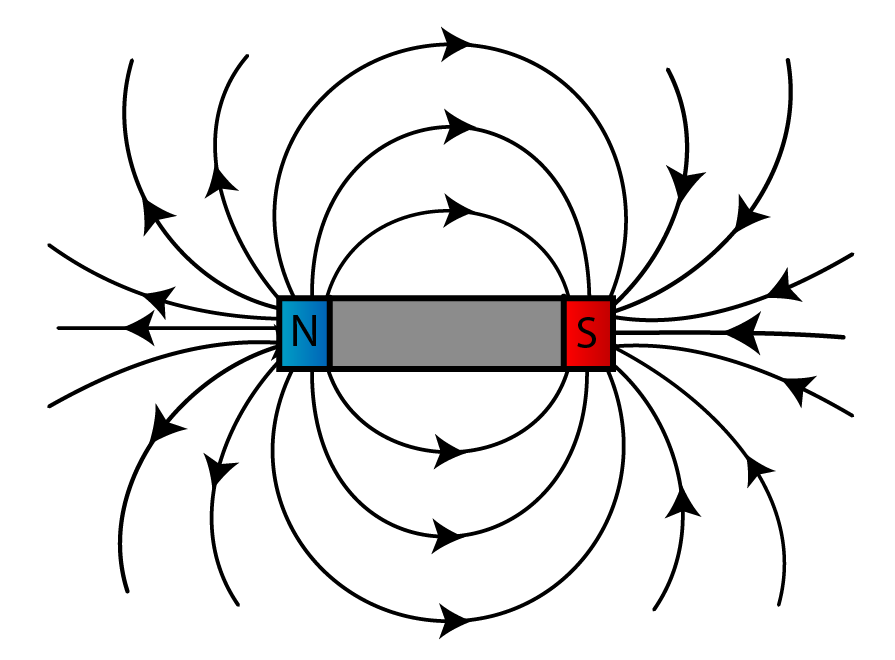
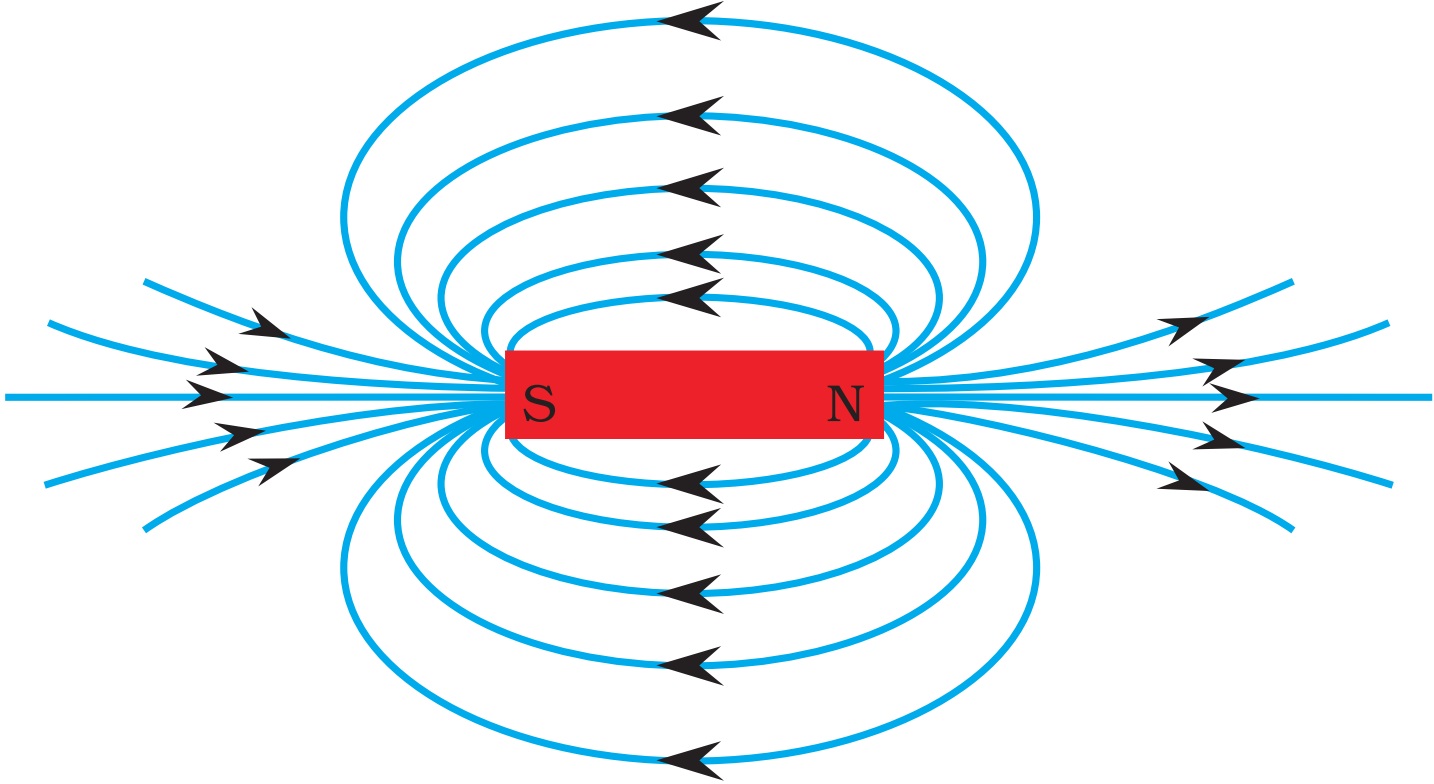
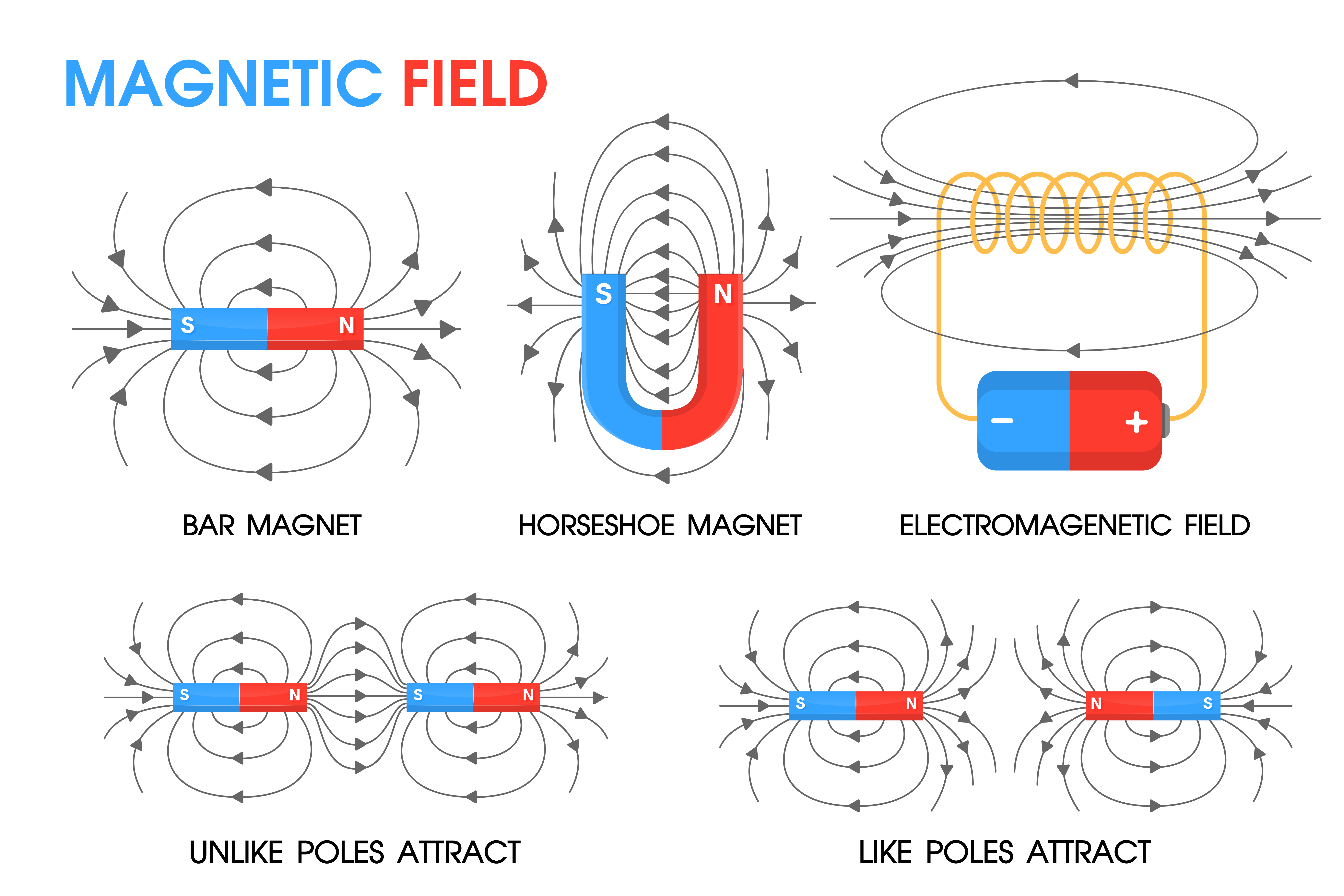
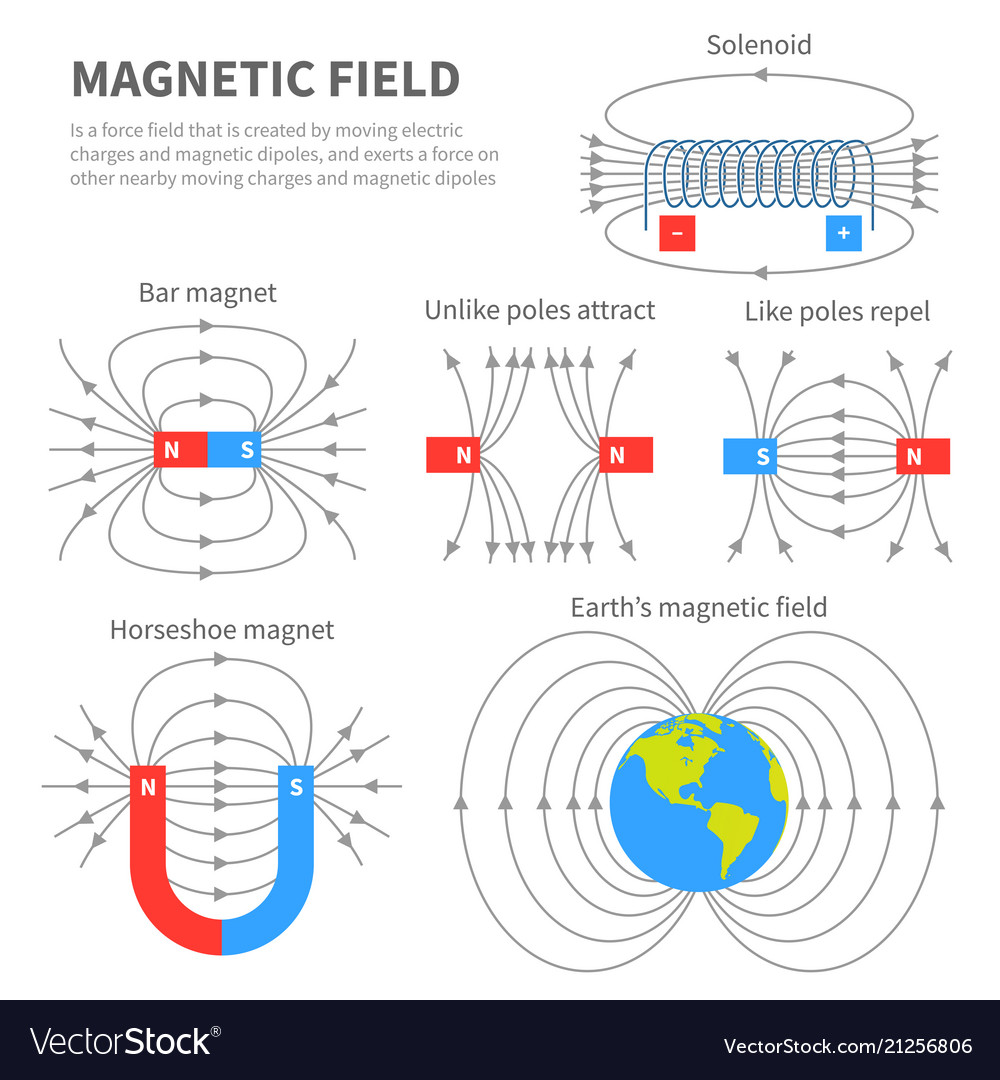
Magnetic field diagrams. Magnetic fields are represented by diagrams which show patterns of magnetic field lines. The magnetic field lines show the direction in which the magnetic force is acting at any particular point. The density of the magnetic field lines shows the strength of the magnetic force acting. If the lines are close together the.
9.3 Earth’s Field Physical Geology
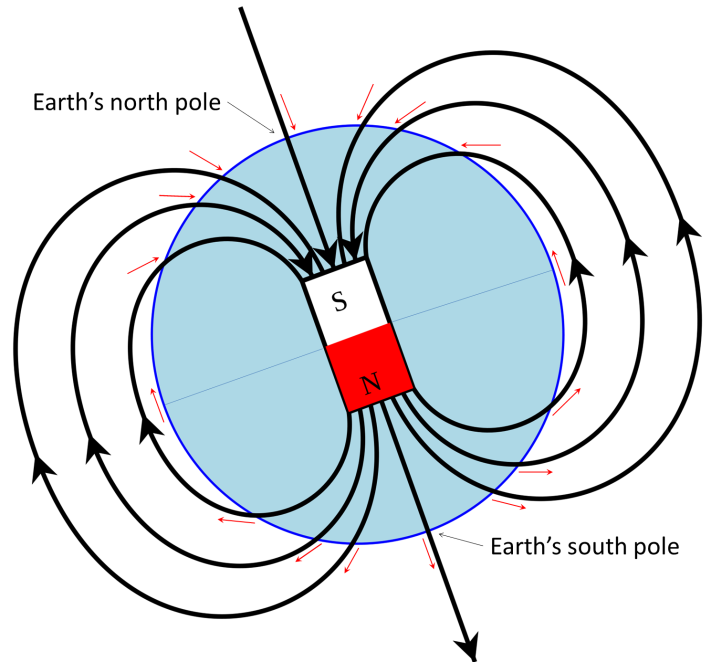
The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo.

Fields, Forces, & Effects Britannica
Example 11.3.1 11.3. 1: An Alpha-Particle Moving in a Magnetic Field. An alpha-particle (q = 3.2 ×10−19C) ( q = 3.2 × 10 − 19 C) moves through a uniform magnetic field whose magnitude is 1.5 T. The field is directly parallel to the positive z -axis of the rectangular coordinate system of Figure 11.3.2 11.3. 2.

La Direction 333 2012 Pole Reversal Happens All The (Geologic) Time
Earth's magnetic field — also known as the geomagnetic field — is generated in our planet's interior and extends out into space, creating a region known as the magnetosphere.
Physics 12 Field and Force
A further difference between magnetic and electric forces is that magnetic fields do not net work, since the particle motion is circular and therefore ends up in the same place. We express this mathematically as: W = ∮B ⋅ dr = 0 (21.4.5) (21.4.5) W = ∮ B ⋅ d r = 0.

Lightning and the Sun's Field NaturPhilosophie
The time for the charged particle to go around the circular path is defined as the period, which is the same as the distance traveled (the circumference) divided by the speed. Based on this and Equation, we can derive the period of motion as. T = 2πr v = 2π v mv qB = 2πm qB. (11.4.3) (11.4.3) T = 2 π r v = 2 π v m v q B = 2 π m q B.

Earth field diagram Royalty Free Vector Image
Either moving a wire through a magnetic field or (equivalently) changing the strength of the magnetic field over time can cause a current to flow. How is this described? There are two key laws that describe electromagnetic induction: Faraday's law, due to 19ᵗʰ century physicist Michael Faraday.
Field Diagram
The diagram shows the magnetic field around a bar magnet. The diagram shows these key features: the magnetic field lines never cross each other the closer the lines, the stronger the.
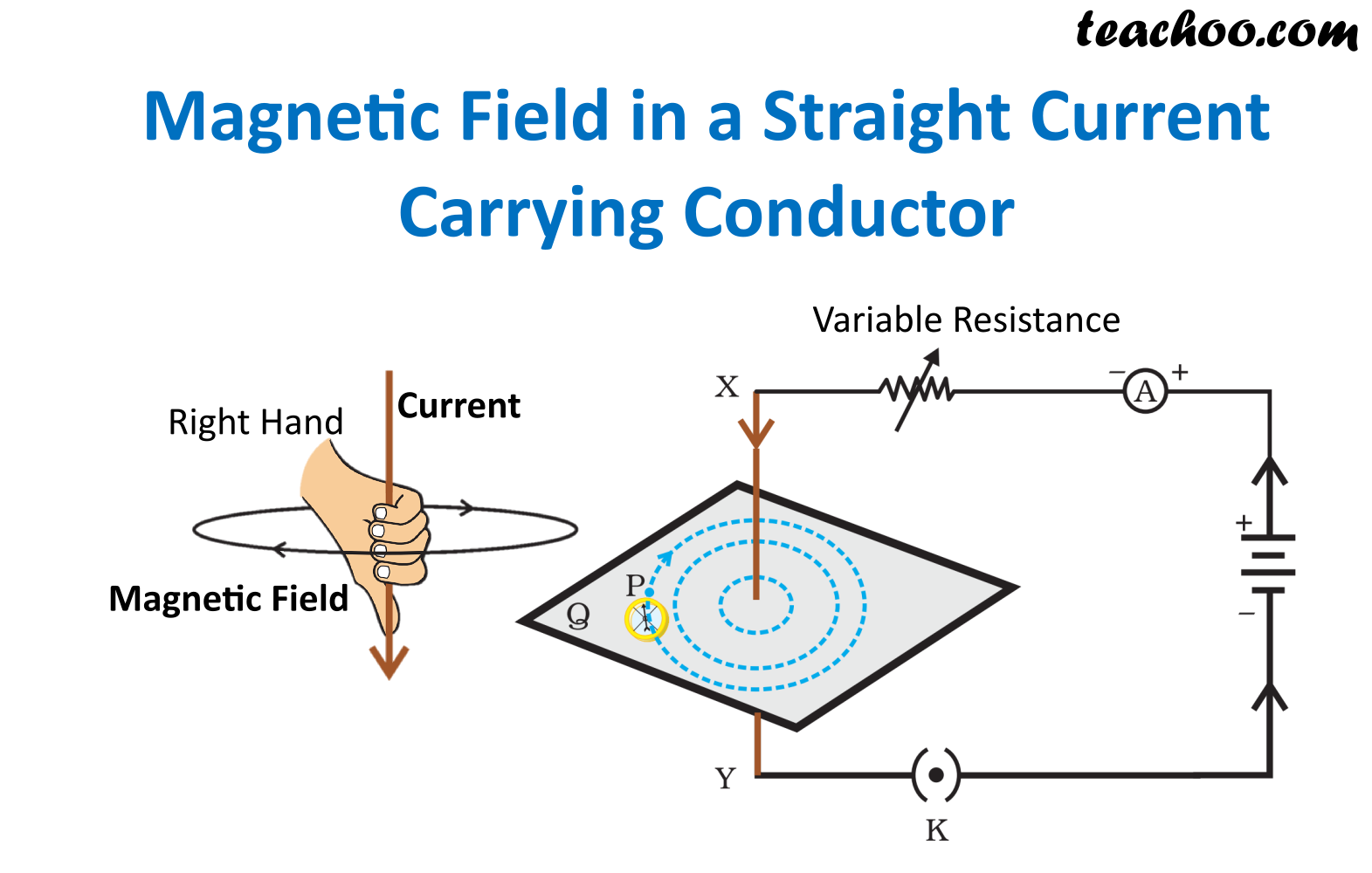
Field Due to Straight Current Carrying Conductor Teachoo
Chapter 27 - Magnetic Field and Magnetic Forces. A moving charge or collection of moving charges (e.g. electric current) produces a magnetic field. (Chap. 28). A second current or charge responds to the magnetic field and experiences a magnetic force. (Chap. 27). Permanent magnets: exert forces on each other as well as on unmagnetized Fe pieces.